
Cat Teeth Diagrams: Understanding Your Cat’s Dental Health – Copy
- March 19, 2025
Table of Contents
A cat teeth diagram is an essential tool for understanding the complex dental structure of a cat, which is crucial for both cat owners and veterinary professionals. The teeth of cats play a vital role in their ability to eat, groom, and communicate. By learning about the cat’s dental anatomy, owners can ensure their pets maintain optimal oral health, preventing common dental problems that can affect their overall well-being.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the cat teeth diagram, from its anatomy to common dental diseases, and how to care for your cat’s teeth.
What is a Cat Teeth Diagram?
A cat teeth diagram is a detailed representation of the various teeth found in a cat’s mouth. It visually illustrates the different types of teeth, their locations, and the functions they serve. These diagrams are widely used by veterinarians, cat owners, and researchers to understand and monitor the health of a cat’s teeth and mouth.
It provides a clear depiction of the adult and kitten dental structures, helping people identify potential issues and ensure their pet’s dental hygiene is well-maintained.
Importance of the Cat Teeth Diagram
The cat teeth diagram is particularly useful for identifying the following:
- The number and arrangement of teeth.
- The differences between kitten and adult teeth.
- Identifying symptoms of common dental issues, such as tooth decay, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
- Monitoring the progress of dental treatments, such as tooth extraction or cleaning.
- Understanding the development of a cat’s teeth from kittenhood to adulthood.
By being familiar with the cat teeth diagram, pet owners can spot issues early, leading to more effective dental care.
Anatomy of a Cat’s Teeth
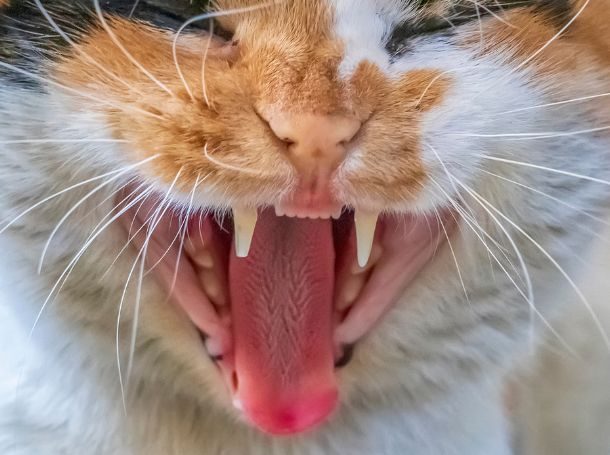

Understanding the anatomy of a cat’s teeth is the first step in interpreting the cat teeth diagram. Cats have a highly specialized set of teeth adapted to their carnivorous diet. Their teeth help them tear and shear meat, and they are equipped with both sharp and grinding surfaces.
Types of Teeth in Cats
Cats have four different types of teeth, each serving a specific purpose. The cat teeth diagram clearly distinguishes these teeth and their roles.
1. Incisors
- Location: Found at the front of the mouth, both on the upper and lower jaws.
- Function: Incisors are small, sharp teeth used for gripping and cutting food into smaller pieces. They also play a key role in grooming by helping cats clean their fur.
- Number: A cat typically has 12 incisors (6 on the top and 6 on the bottom).
2. Canines (Fangs)
- Location: Positioned next to the incisors, the canine teeth are longer and sharper than the other teeth.
- Function: The primary role of the canines is to catch and hold prey. These teeth are essential for hunting and self-defense.
- Number: Cats have 4 canine teeth, 2 on the top and 2 on the bottom.
3. Premolars
- Location: Located behind the canines, the premolars are slightly smaller than the molars but still play an essential role in cutting and grinding food.
- Function: Premolars are used to tear and crush food, especially meat and bone. They help break down food into smaller, digestible pieces.
- Number: Cats have 10 premolars, 6 on the upper jaw and 4 on the lower jaw.
4. Molars
- Location: Molars are the last teeth at the back of the mouth, behind the premolars.
- Function: Molars are used for grinding and crushing food. They help break down harder substances, like bone, that cats consume in the wild.
- Number: Cats have 4 molars, 2 on the upper jaw and 2 on the lower jaw.
Summary of Tooth Functions in Cats
Each type of tooth has a unique function that reflects a cat’s carnivorous diet. From cutting and tearing to grinding and crushing, cats rely on their specialized teeth to consume and process their food efficiently. Understanding these functions is critical when interpreting the cat teeth diagram.
The Development of Cat Teeth
Cats go through different stages of teeth development. Their teeth grow and change as they age, and understanding these changes is important for monitoring their dental health.
Kitten Teeth Development
Kittens are born without teeth, but by around 2 to 3 weeks of age, their first set of baby teeth (deciduous teeth) begin to emerge. These teeth will eventually fall out as the kitten’s permanent teeth come in. The teething process in kittens typically occurs between 3 and 6 months of age.
Timeline of Kitten Teeth Development:
- 2-3 Weeks: The first set of incisors appears.
- 3-4 Weeks: Canine teeth start to emerge.
- 4-6 Weeks: Premolars begin to develop.
- 6 Months: The baby teeth fall out and are replaced by permanent adult teeth.
During this time, it’s crucial to monitor a kitten’s teeth for signs of issues like overcrowding or premature tooth loss.
Adult Teeth Development
By the time a cat reaches 7 to 8 months of age, they will have a full set of adult teeth. These teeth will remain throughout their adult life, typically until they reach around 10 years of age, after which some may begin to wear down or fall out due to age-related conditions.
Common Dental Problems in Cats
Just like humans, cats can experience a variety of dental issues that can affect their overall health. Regular check-ups and understanding the cat teeth diagram can help identify these problems early.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is one of the most common dental problems in cats. It occurs when plaque and tartar build up on the teeth, leading to gum inflammation, pain, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
- Symptoms: Bad breath, swollen gums, difficulty eating, and visible tartar buildup.
- Prevention: Regular brushing, professional cleanings, and dental chews can help prevent periodontal disease.
Tooth Decay
While less common than in humans, tooth decay can still affect cats. Decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth create acids that erode the enamel, leading to cavities.
- Symptoms: Visible holes in the teeth, pain while eating, and difficulty chewing.
- Prevention: Routine dental care and monitoring a cat’s diet can help prevent tooth decay.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, where the gums become inflamed due to plaque buildup. It can progress to more severe periodontal disease if not treated.
- Symptoms: Red and swollen gums, bleeding when the cat eats or when the gums are touched.
- Prevention: Regular brushing and professional cleanings can prevent gingivitis.
Tooth Loss
Cats may lose their teeth as they age or due to untreated dental disease. While some tooth loss is a natural part of aging, early intervention can prevent unnecessary extractions.
- Symptoms: Difficulty chewing, dropping food, and noticeable tooth loss.
- Prevention: Regular veterinary check-ups can help prevent unnecessary tooth loss.
How to Care for Your Cat’s Teeth
Proper dental care is essential to maintaining the health of your cat’s teeth and gums. The cat teeth diagram provides a visual reference to help you understand the specific teeth that may need attention.
Brushing Your Cat’s Teeth
The best way to prevent dental issues is by brushing your cat’s teeth regularly. While it may take time for your cat to adjust to brushing, it is the most effective way to reduce plaque buildup.
- How to Brush: Use a soft toothbrush and toothpaste formulated for cats. Gently brush in circular motions, focusing on the outer surfaces of the teeth.
Dental Chews and Toys
Dental chews and toys are excellent for keeping your cat’s teeth clean between brushings. These chews help scrape away plaque and tartar, keeping their teeth in good condition.
Professional Dental Care
In addition to at-home care, cats should receive professional dental cleanings from a veterinarian. During these cleanings, the vet will remove tartar buildup and check for signs of disease or decay.
Diet and Nutrition
Feeding your cat a balanced diet, including dry food and special dental diets, can help keep their teeth clean. Some foods are designed specifically to reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
Conclusion
A cat teeth diagram is an invaluable resource for understanding the dental anatomy of cats. By familiarizing yourself with this diagram, you can ensure that your cat receives the best dental care possible, preventing common dental issues and maintaining their overall health. Regular brushing, professional cleanings, and a balanced diet are all essential components of good dental care. Whether you’re a new cat owner or a seasoned one, knowing how to care for your cat’s teeth will help them live a longer, healthier life.
Regularly referring to the cat teeth diagram will not only help you understand your cat’s dental health but will also enable you to detect any potential issues early. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, so start a dental care routine today to ensure your cat’s smile stays bright and healthy for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Adult cats typically have 30 teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, arranged for tearing and grinding food.
Kittens start to lose their baby teeth at around 3 to 4 months old, and their permanent adult teeth usually emerge by 6 to 7 months.
Periodontal disease is a common dental issue in cats, caused by plaque buildup that leads to gum inflammation, tooth decay, and even tooth loss.
Regular brushing, dental chews, professional vet cleanings, and a healthy diet can help maintain your cat’s dental health and prevent problems.
Understanding the cat teeth diagram helps pet owners identify dental issues early, maintain good oral hygiene, and seek timely veterinary care.




Leave a comment